The Mohs scale is an empirical criterion for evaluating the hardness of materials. It takes its name from the German mineralogist Friedrich Mohs , who conceived it in 1812 . It takes as a reference the hardness of ten minerals numbered progressively from 1 to 10, such that each is able to scratch what precedes it and is scratched by what follows it. To determine the hardness of a mineral one does nothing other than prove which mineral of the scale it scratches and from which it is scratched.
The first mineral of the series is the talc , the last the diamond . The Mohs scale provides a purely indicative value of hardness, as the actual difference in hardness between two successive minerals also varies considerably. For example corundum (n. 9 of this scale) is about six times harder than topaz (n. 8), while diamond (n. 10) appears to be about 140 times harder than corundum, as has been pointed out from the experimental tests of the mineralogist August Rosiwal .
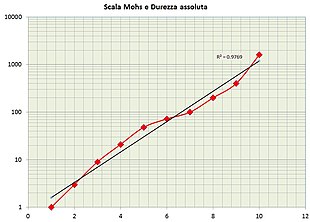
There is also an absolute scale of hardness, the Rosiwal scale , which provides the real value of hardness, obtained with laboratory tests using a sclerometer . In this scale it is attributed to corundum (a mineral that includes many precious stones, including ruby and sapphire ) a reference hardness of 1,000.
Index
The Mohs scale in practice [ edit | edit wikitesto ]
| Guy | Hardness of Mohs | Mineral | Chemical formula | Absolute hardness[1] | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teneri [T 1] | 1 | Talc | Mg 3 Si 4 O 10 (OH) 2 | 1 |  |
| 2 | Plaster | CaSO 4 · 2H 2 O | 3 |  | |
| Semi-hard[T 2] | 3 | Calcite | CaCO 3 | 9 |  |
| 4 | Fluorite | CaF 2 | 21 |  | |
| 5 | Apatite | Ca 5 (PO 4 ) 3 (OH - , Cl - , F- ) | 48 |  | |
| Hard [T 3] | 6 | Ortoclasio | KAlSi 3 O 8 | 72 |  |
| 7 | Quartz | SiO 2 | 100 |  | |
| 8 | Topaz | Al 2 SiO 4 (OH - , F - ) 2 | 200 |  | |
| 9 | corundum | Al 2 O 3 | 400 |  | |
| 10 | Diamond | C | 1600 |  | |
To give some examples, in this scale the hardness of a nail is 2.2, of the tip of a steel knife from 5.1 to 5.5, of window glass from 5.6 to 6.5, of an iron file of about 6.5, of porcelainfrom 6 to 7; some types of ceramics , including porcelain stoneware , can reach hardness 8.
Intermediate levels [ edit | edit wikitesto ]
The following table shows the various intermediate levels.

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar